目录
变量
变量种类
- 实例变量:独立方法之外的非static变量
- 类变量:独立方法之外的static变量
- 局部变量:方法中的变量
- 参数:方法后面括号类的参数
命名规则
- 变量名区别大小写,以字母、$、_ 开头,后面为字母,数字,$和_。人们习惯以字母开头命名变量
- 变量名不能包含关键字和保留字段
- 建议命名遵循驼峰式命名规则,一个单词时变量全部小写,两个单词以上组成,第二个开始首字母大写;常量建议全部大写,每个单词以下划线隔开
基本数据类型
Java共有八中基础数据类型
| 类型 | 字节 | 取值范围 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| byte | 8 | -2^7 ~ 2^7-1 | 0 |
| short | 16 | -2^15 ~ 2^15-1 | 0 |
| int | 32 | -2^31 ~ 2^31-1 | 0 |
| long | 64 | -2^63 ~ 2^63-1 | 0L |
| float | 32 | / | 0.0f |
| double | 64 | / | 0.0d |
| char | 16 | \u0000 ~ \uffff | ‘\u0000’ |
| boolean | / | true/false | false |
Java SE 7及以上的版本可以在数字之间加上下划线,但需要遵守以下规则
- 在数字的开头和结尾不能使用
- 于浮点类型的小数点附件
- 在F、L等尾缀之前
- 在需要一串数字的地方
数组
数组是一个对象容器,类型相同,个数固定
下列代码演示创建一个数组,给数组复制,打印数组
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declares an array of integers
int[] anArray;
// allocates memory for 10 integers
anArray = new int[10];
// initialize first element
anArray[0] = 100;
// initialize second element
anArray[1] = 200;
// and so forth
anArray[2] = 300;
anArray[3] = 400;
anArray[4] = 500;
anArray[5] = 600;
anArray[6] = 700;
anArray[7] = 800;
anArray[8] = 900;
anArray[9] = 1000;
for (int i = 0 ; i < anArray.length ; i++) {
System.out.println("Element at index "+i+":"+
+ anArray[i]);
}
}
}
输出如下图所示
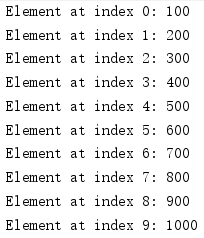
声明一个数组需要使用[],该符号可以放在类型后面,也可以放在变量后面
float[] anArray;
float anArray[];
声明只是声明一个数组,并不是创建一个数组
创建一个数组需要使用new关键字,例如ArrayDemo中创建一个int数组
数组的初始化既可以如ArrayDemo一个一个赋值,也可以以如下方式赋值
int[] anArray = {
100, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600,
700, 800, 900, 1000
};
数组的大小由大括号内的逗号相隔的值的数量决定
复制数组
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length)
从src的第srcPos个元素开始复制(length-destPos)个元素到数组dest的destPos和length
public class ArrayCopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] copyFrom = { 'd', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e',
'i', 'n', 'a', 't', 'e', 'd' };
char[] copyTo = new char[7];
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
System.out.println(new String(copyTo));
}
}
输出如下图所示
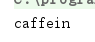
数组操作
- 复制数组copyOfRange
- 获取数组中特定值的位置binarySearch
- 比较两个数组 equals
- 用特定值填充数组 fill
- 按升序进行排序sort,Java SE
运算符
优先级(由高到低)
| 运算符 | 优先度 |
|---|---|
| postfix | expr++ expr– |
| unary | ++expr –expr +expr -expr ~ ! |
| multiplicative | * / % |
| additive | + - |
| shift | « » »> |
| relational | < > <= >= instanceof |
| equality | == != |
| bitwise AND | & |
| bitwise exclusive OR | ^ |
| bitwise inclusive OR | | |
| logical AND | && |
| logical OR | || |
| ternary | ? : |
| assignment | = += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= «= »= »>= |
赋值、算术、一元运算
赋值运算“=”:将右边的值赋值给左边
int i = 0;
boolean b = false;
算术运算“+、-、*、/、%”,用法如下所示
class ArithmeticDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int result = 1 + 2;
// result is now 3
System.out.println("1 + 2 = " + result);
int original_result = result;
result = result - 1;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " - 1 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result * 2;
// result is now 4
System.out.println(original_result + " * 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result / 2;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " / 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result + 8;
// result is now 10
System.out.println(original_result + " + 8 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result = result % 7;
// result is now 3
System.out.println(original_result + " % 7 = " + result);
}
}
’=’其他用法: 和其他运算符结合,比如上述代码可以改写成:
class ArithmeticDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int result = 1 + 2;
// result is now 3
System.out.println("1 + 2 = " + result);
int original_result = result;
result -= 1;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " - 1 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result *= 2;
// result is now 4
System.out.println(original_result + " * 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result /= 2;
// result is now 2
System.out.println(original_result + " / 2 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result += 8;
// result is now 10
System.out.println(original_result + " + 8 = " + result);
original_result = result;
result %= 7;
// result is now 3
System.out.println(original_result + " % 7 = " + result);
}
}
’+’其他用法: 拼接字符串
class ConcatDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
String firstString = "This is";
String secondString = " a concatenated string.";
String thirdString = firstString+secondString;
System.out.println(thirdString);
}
}
输出结果为:
This is a concatenated string.
一元运算符
- ’+’一元加运算符,表示正值
- ’-‘一元减运算符,对一个数值取反值
- ’++(–)’自增(减)运算符,讲一个数值加(减)1
- ’!’布尔值反转,和逻辑补运算
class UnaryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = +1;
// result is now 1
System.out.println(result);
result--;
// result is now 0
System.out.println(result);
result++;
// result is now 1
System.out.println(result);
result = -result;
// result is now -1
System.out.println(result);
boolean success = false;
// false
System.out.println(success);
// true
System.out.println(!success);
}
}
++x(–x)和x++(x–)的区别
这两者的区别体现在复合表达式当中,++x(–x)先加(减)1,在参与运算;x++(x–)先参与运算,在改变值
class PrePostDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 3;
i++;
// prints 4
System.out.println(i);
++i;
// prints 5
System.out.println(i);
// prints 6
System.out.println(++i);
// prints 6
System.out.println(i++);
// prints 7
System.out.println(i);
}
}
关系运算符
- ==
- !=
- >
- >=
- <
- <=
条件运算符
- &&,逻辑与,表示两边都为true才为true
- ||,逻辑或,表示两边其中一个为true就为true
- 布尔类型表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2,布尔类型表达式为true去表达式1否则为2
类型比较运算符 instanceof
instanceof可以将对象与指定类型进行比较,可以用来测试对象是否为类或子类的实例,以及接口的实现类的实例
位操作符和位移操作符
操作符为 ~ « » »> & ^ |
控制语句
if-then-else 和 if-then 语句
if-then语句只有在条件为true时,才会执行特定的代码段
void testIf() {
boolean testEvaluates = true;
if (testEvaluates){
System.out.println("testEvaluates is true");
}
}
if-then-else语句,在条件为true时执行if后面的代码段,否则执行else后面的代码段
void testIfElse() {
boolean testEvaluates = true;
if (testEvaluates){
System.out.println("testEvaluates is true");
} else {
System.out.println("testEvaluates is not true");
}
}
上面代码只是if-then-else的基本应用
该控制条件还可以像下面示例一样
下面代码在满足适合条件,就不会执行其他语句
class IfElseDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testscore = 76;
char grade;
if (testscore >= 90) {
grade = 'A';
} else if (testscore >= 80) {
grade = 'B';
} else if (testscore >= 70) {
grade = 'C';
} else if (testscore >= 60) {
grade = 'D';
} else {
grade = 'F';
}
System.out.println("Grade = " + grade);
}
}
switch
switch语句目前支持byte、short、char、int、Enum Type、String、Character,、Byte、Short以及Integer
具体用法如下
public class SwitchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 8;
String monthString;
switch (month) {
case 1: monthString = "January";
break;
case 2: monthString = "February";
break;
case 3: monthString = "March";
break;
case 4: monthString = "April";
break;
case 5: monthString = "May";
break;
case 6: monthString = "June";
break;
case 7: monthString = "July";
break;
case 8: monthString = "August";
break;
case 9: monthString = "September";
break;
case 10: monthString = "October";
break;
case 11: monthString = "November";
break;
case 12: monthString = "December";
break;
default: monthString = "Invalid month";
break;
}
System.out.println(monthString);
}
}
最终输出
August
每个case后面都有一个break,这样可以在执行适合条件的语句块后跳出switch语句块,如果不加break,则在执行适合的语句块后一直执行语句
while 和 do-while
while如下所示,当expression为true时会一直执行while代码块知道expression为false
while (expression) {
statement(s)
}
do-while如下所示,他先执行代码块,在判断expression,为true继续执行代码块,知道expression为false
do {
statement(s)
} while (expression);
他们两个区别在于,do-while至少会执行一次
for语句
for语句现在有两种方式
//通常for循环
for (initialization; termination;
increment) {
statement(s)
}
//增强型for循环
for(元素类型 元素名称 : 遍历数组(集合)(或者能进行迭代的)){
statement(s)
}
上述两种方式都可以实现for循环,推荐第二种实现方式
class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] numbers = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for(int i=1; i<numbers.length; i++){
System.out.println("Count is: " + numbers[i]);
}
for (int item : numbers) {
System.out.println("Count is: " + item);
}
}
}
分支语句break和continue
break跳出当前循环 continue忽略本次循环,继续执行下一次循环 标签,可以让break跳出循环到标签位置,结束迭代;continue跳过用给定标签标记的外部循环的当前迭代,开始下次迭代
class ContinueWithLabelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String searchMe = "Look for a substring in me";
String substring = "sub";
boolean foundIt = false;
int max = searchMe.length() -
substring.length();
test:
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++) {
int n = substring.length();
int j = i;
int k = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (searchMe.charAt(j++) != substring.charAt(k++)) {
continue test;
}
}
foundIt = true;
break test;
}
System.out.println(foundIt ? "Found it" : "Didn't find it");
}
}
return
return 退出当前方法